Qadirabad, a historically significant village in Pakistan’s Punjab province, is located right next to the Chenab River. It is situated in the Phalia tehsil of the Mandi Bahauddin District. The land promises a trip of culture, scenic beauty, and the friendliness of its people. It provides a window into rural Punjab.
For more details about the village of Qadirabad, visit Graana.com.
Highlights
| Feature | Value |
| Coordinates | 32°17′51″N 73°30′07″E |
| Country | Pakistan |
| Region | Punjab |
| District | Mandi Bahauddin |
| Tehsil | Phalia |
Location
In Pakistan’s Punjab District’s Mandi Bahauddin District, Qadirabad reveals its allure. The settlement is situated near the Phalia town administration centre because it is part of the Phalia tehsil.
More significantly, Qadirabad is beautifully situated close to Pakistan’s main river, the Chenab River. The village’s growth was probably influenced by its closeness to the river, which may also have impacted its farming methods.
Information indicates that there may be a connection to the motorway network for the surrounding roads. Some sites also highlight having access to Motorway M-3, which might provide links to the area’s bigger cities.
Furthermore, Qadirabad may be connected to neighbouring towns and villages in the Phalia tehsil by local roads.
How to Reach Qadirabad?
Below is a summary of the options you can choose from to reach Qadirabad:
By Car
- The Lahore-Islamabad Motorway (M-2) provides a quicker route from major cities, particularly Islamabad and Lahore. After leaving M-2 at Bhera Phuarwan Road, go to Sargodha and Gujrat by following the signs. Eventually, you will come to Mandi Bahauddin Road, which goes towards Qadirabad.
- Grand Trunk Road (GT Road): Due to traffic, this historic route may be slower but offers a more picturesque path. From where you are now, take the GT Road and proceed as directed by the signage to Mandi Bahauddin. Proceed to Phalia and then Qadirabad from Mandi Bahauddin.
Through Public Transport
- Bus: Several bus companies provide routes from Mandi Bahauddin to neighbouring cities and towns. Check with the nearby bus terminals for information on bus timetables and availability for Phalia. From there, take a local rickshaw to Qadirabad.
- Train: Mandi Bahauddin is home to the closest train station. Travel by train to Mandi Bahauddin, and then finish your trip to Qadirabad by hiring a rickshaw or taxi.
By Air
- The distance to Sialkot International Airport (SKT) is about 115 km. After a car or taxi after you arrive.
- A little over 210 kilometres separate Allama Iqbal International Airport (LAHORE) from Qadirabad.
Popular Places Near Qadirabad

Because Qadirabad is small, there are only a few significant attractions nearby.
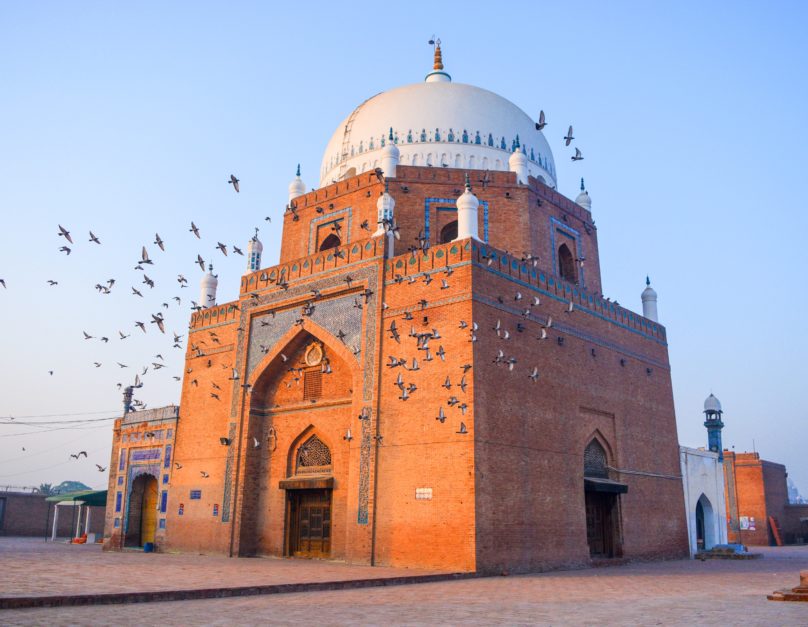
- The Mausoleum of Bahauddin Zakariya and the Multan Museum are located in this historic city of Multan, which is a must-visit for anybody interested in learning more about Pakistan’s rich cultural heritage. The museum provides an intriguing view of the area’s history, and the mausoleum is a noteworthy monument.
- Shan Rukn-e-Alam Shrine: Another vital landmark in Multan, this shrine is a well-liked hangout for tourists and pilgrims drawn to holy places and striking architectural design.
- Mausoleum of Bahauddin Zakariya: This exquisite shrine, located in Multan, honours the Sufi saint Bahauddin Zakariya. For those interested in Pakistani history and culture, the mausoleum is a must-see, ranking among Multan’s most significant sites.
- Multan Museum: Also in Multan, this museum houses a fascinating collection of artefacts and exhibits that showcase the region’s rich history and culture. You’ll find pieces spanning various eras, offering a glimpse into the development of this part of Pakistan.
- Chenab River: The Chenab River flows close to Qadirabad, providing beautiful scenery for outdoor enthusiasts. Savour a picnic by the river, take a boat excursion, or take in the beauty of the surrounding environment.
Qadirabad’s Surroundings

From Qadirabad, several towns and cities are conveniently located. The nearest city is Phalia, which is around twenty kilometres distant. The district capital, Mandi Bahauddin, is around forty kilometres away. Gujrat is about 70 kilometres away for a more expansive city experience.
Here are some distances to help you with your itinerary:
- Two routes to Sargodha are available. The first option travels roughly 98 km through Bhalwal, and the second option travels roughly 104 km through Sial Mor.
- Faisalabad: 165 km can be travelled to get to Faisalabad via the M-3 motorway.
- Lahore: Various methods are available to access the Allama Iqbal International Airport in Lahore. The drive through Gujranwala is about 180 kilometres, whereas the motorway route is about 210 km. There are two routes via Gujranwala: the motorway route is roughly 185 kilometres long, and the traditional Ravi bridge route is about 150 kilometres long.
- Islamabad: There are three routes to reach the Islamabad International Airport. The motorway route is roughly 255 kilometres long, and the routes through Gujrat and Mandi Bahauddin are about 200 and 230 km long, respectively.
- Hafizabad: The Qadirabad headworks route leads to this city, which is about 65 km away.
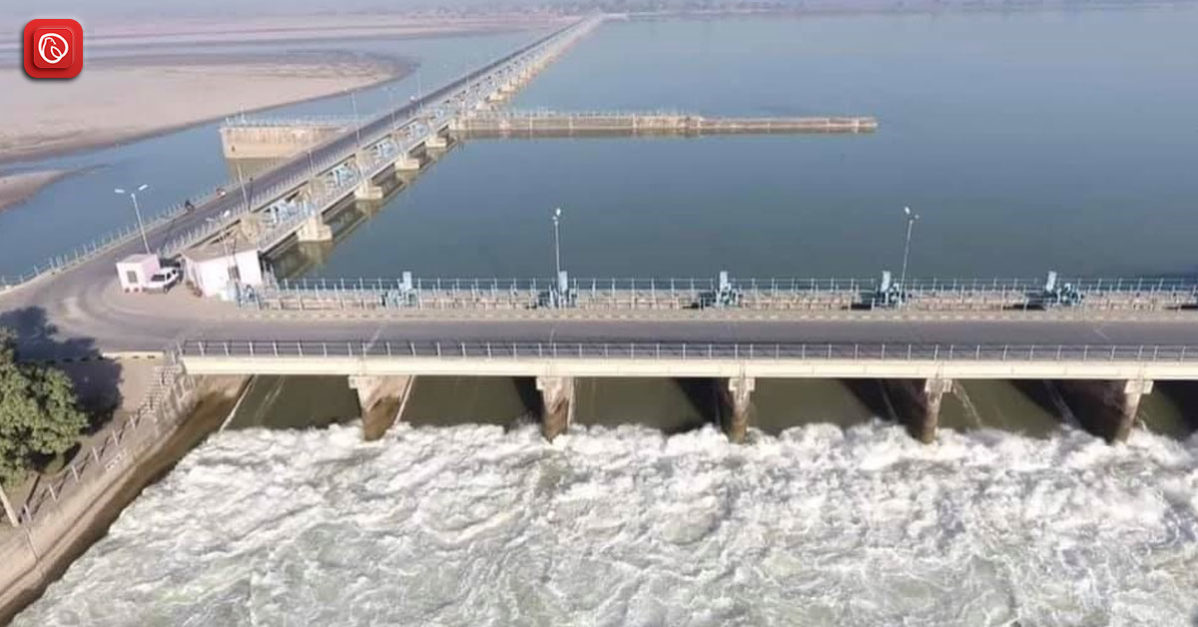
The Qadirabad Barrage
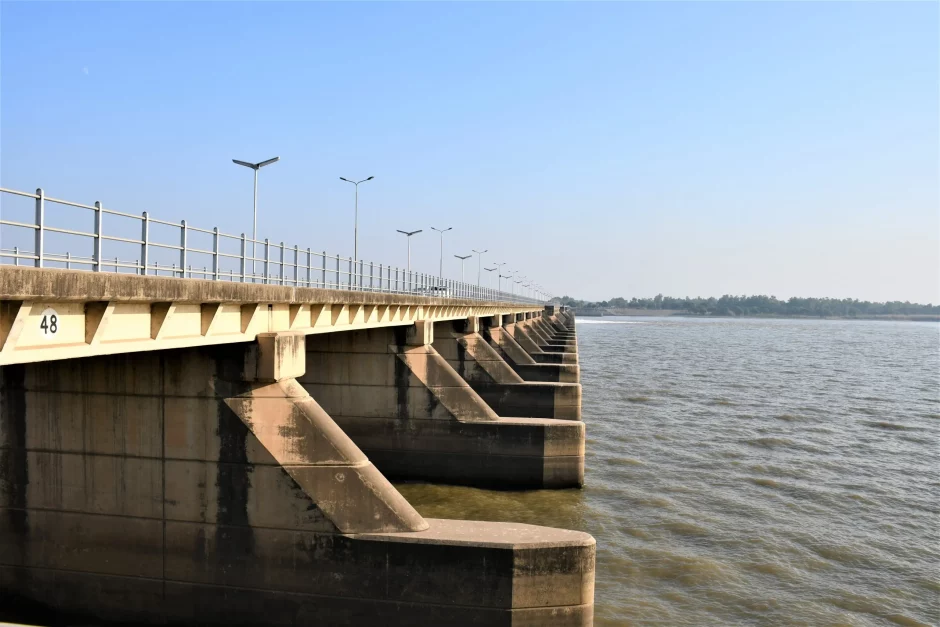

In Pakistan’s Punjab region, the Qadirabad Barrage is a notable engineering marvel on the Chenab River. More than just a building, it is the cornerstone of the area’s agricultural success story.
A Legacy of Engineering
Built as a component of the Indus Basin Project, the Qadirabad Barrage has a distinguished past. Constructed in the mid-1900s, it bears witness to the vision and technical mastery of the time.
Encompassing more than 3,300 feet and featuring 50 distinct bays, the barrage controls the course of the Chenab River, guaranteeing an essential water source for the adjacent regions.
Taming the River, Nurturing the Land
An important part of water management is the Qadirabad Barrage. By managing the flow of the Chenab River, it diverts water into agricultural canals while simultaneously preventing flooding during intense monsoon seasons.
This diverted water nourishes large stretches of farmland, which is vital to the agricultural industry. With a planned capacity of 9 million cusecs, the barrage has enormous potential for irrigating large areas of land.
Beyond Irrigation

The Qadirabad Barrage’s importance goes beyond its use in farming. It is an essential head regulator for the Rasul-Qadirabad-Baloki-Sulemanki Link Canal System. It is a vital water distribution network spanning a larger area. Furthermore, the barrage may aid in the production of hydropower. However, further data is required to make this claim with certainty.
A Symbol of Progress
The Qadirabad Barrage, towering over the Chenab River, is a symbol of Pakistan’s success and development. It represents how human ingenuity has tamed the forces of nature to support prosperity and life. The barrage’s continuous operation guarantees the well-being of innumerable communities that rely on its life-giving waters.
History
The history of Qadirabad emerges like a tale passed down through the ages. The very name of the settlement, “Qadirabad,” conjures up images of Mirza Qadir Khan, whose grave is inside the village walls together with his brother’s.
Travelling back in time, we reach the mid-1600s, when Qadirabad was surrounded by a wall for protection. With its three entrances, this wall represented the community’s resilience and cohesiveness in addition to acting as a physical barrier.
In the twentieth century, Qadirabad is situated in the nexus of a nation’s formation. The village’s predominately Muslim residents enthusiastically backed the Pakistan Movement and the Muslim League. The course of history changed in 1947 when Pakistan gained its independence.
In search of a fresh start, the minority Hindu and Sikh groups immigrated to India. But there was a flip side to this migration.
Like many Pakistani villages, Qadirabad’s history bears witness to its people’s resilience. It’s a tale of resiliency, transformation, and the lasting strength of community.
FAQs on Qadirabad
Here are the FAQs.
Where is Qadirabad located?
Qadirabad is a village in the Phalia tehsil of Mandi Bahauddin District, Punjab province, Pakistan. Its geographical coordinates are 32°17′51″N 73°30′07″E.
What’s the significance of the name Qadirabad?
The village’s name comes from Mirza Qadir Khan, a historical figure believed to be buried alongside his brother in the town.
How can I get to Qadirabad?
While Qadirabad lacks its own airport or train station, several options exist for reaching the village. The nearest railway station is in Mandi Bahauddin town, and several international airports are within driving distance (Lahore, Faisalabad, Sialkot, Islamabad). Upon arrival at any of these airports, you can reach Qadirabad by car or taxi.
What’s interesting to see or do around Qadirabad?
Due to its size, Qadirabad itself might have little attractions. However, the surrounding Mandi Bahauddin District offers historical sites like the Mausoleum of Bahauddin Zakariya and the Multan Museum in Multan City.
What role does the Qadirabad Barrage play?
The Qadirabad Barrage is a crucial structure on the Chenab River. It regulates water flow, preventing floods and diverting water for irrigation purposes. This ensures a vital water supply for the surrounding agricultural lands and contributes to the region’s prosperity.
This was all about Qadirabad. For more information, visit Graana.com.




